Sensational Info About How To Get Rid Of Bacterial Infection

Stay hydrated is necessary to maintain functions of the body.
How to get rid of bacterial infection. If you have mrsa, your doctor will probably prescribe you. Tried a yeast/bv med twice, and am now using boric acid. The beneficial ones, the opportunistic, and the harmful ones.
Use plain yogurt as a suppository to naturally cure your yeast infection. Rest, especially the first few days, to help your body fight the infection. The treatment for bacterial infections is usually a course of antibiotics.
Now, remember that opportunistic bacteria throw themselves at any opportunity. Sinus infection treatment options include: So you can get a bacterial infection through an opening in your skin, such as a cut, a bug bite, or a surgical.
Water can boost immune system and. So you can get a bacterial infection through an opening in your skin, such as a cut, a bug bite, or a surgical. Clean hands prevent the transfer of germs or bacteria to the face and other parts of the body.
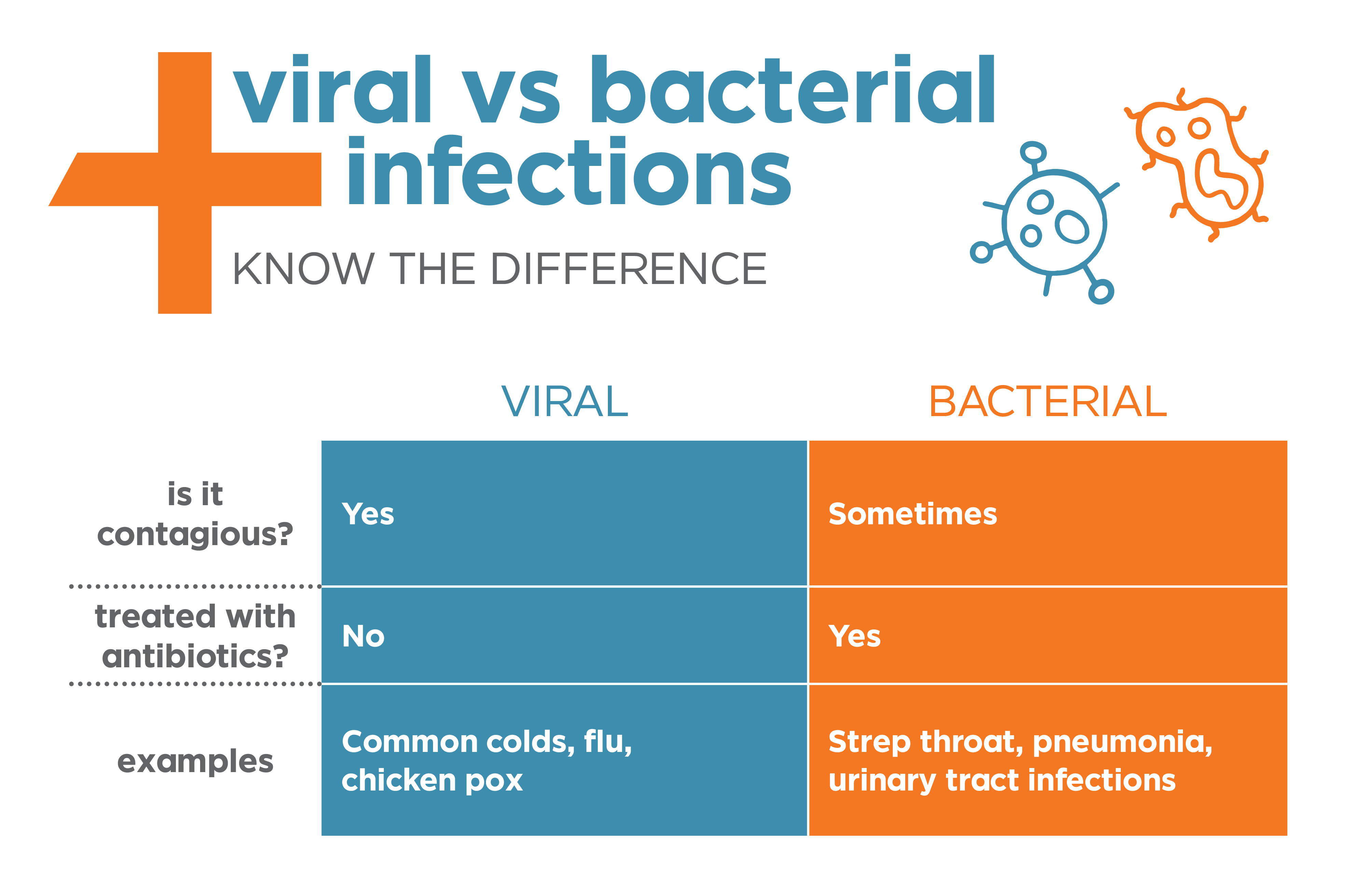
Antibiotics kill all types of bacteria: · then, apply the mixture to the infected skin, let stand for 30 minutes then rinse with warm. How to get rid of a bacterial infection in the vagina that's been going on for over a year?
· take a few crushed garlic cloves, mix well with a teaspoon of olive oil. The good strains of bacteria, like lactobacillus, are essential for maintaining a healthy vaginal flora and preventing infections. How do females get bacterial infections?
Your doctor might prescribe you oral antibiotics, a topical antibiotic ointment, or both. Bacteria must enter your body for them to cause an infection. Having a new sex partner or multiple sex.
The treatment for bacterial infections is usually a course of antibiotics. Bacteria must enter your body for them to cause an infection. Shower after a workout make sure you get rid of the sweat from a work out.
How do you get rid of a bacterial infection in your body? The course of treatment is usually one to six months. Bv is linked to an imbalance of “good” and “harmful” bacteria that are normally found in a woman's vagina.
/bacterial-vaginosis-risk-factors-16-5b0d7390a474be00375b57b7.png)







/what-is-a-bacterial-infection-7705652_final-2f1b8b2429b2495c8333b584512d3afa.jpg)



/bacterial-vaginosis-symptoms-5b58d82fc9e77c0071385390.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Brain-Infection_Illustrator_Sydney-Saporito_Final-08cd4a9c5e22483683d1fa6e984afcc6.jpg)
